Implement proactive measures to comply with the world’s most comprehensive data privacy law and build a sustainable culture of trust for your organization.
Solutions for GDPR Compliance
Operationalize compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation
Demonstrate accountability for the EU’s GDPR requirements and enforce the governance of these policies and principles across your data landscape with OneTrust, an official Europrivacy technology partner.
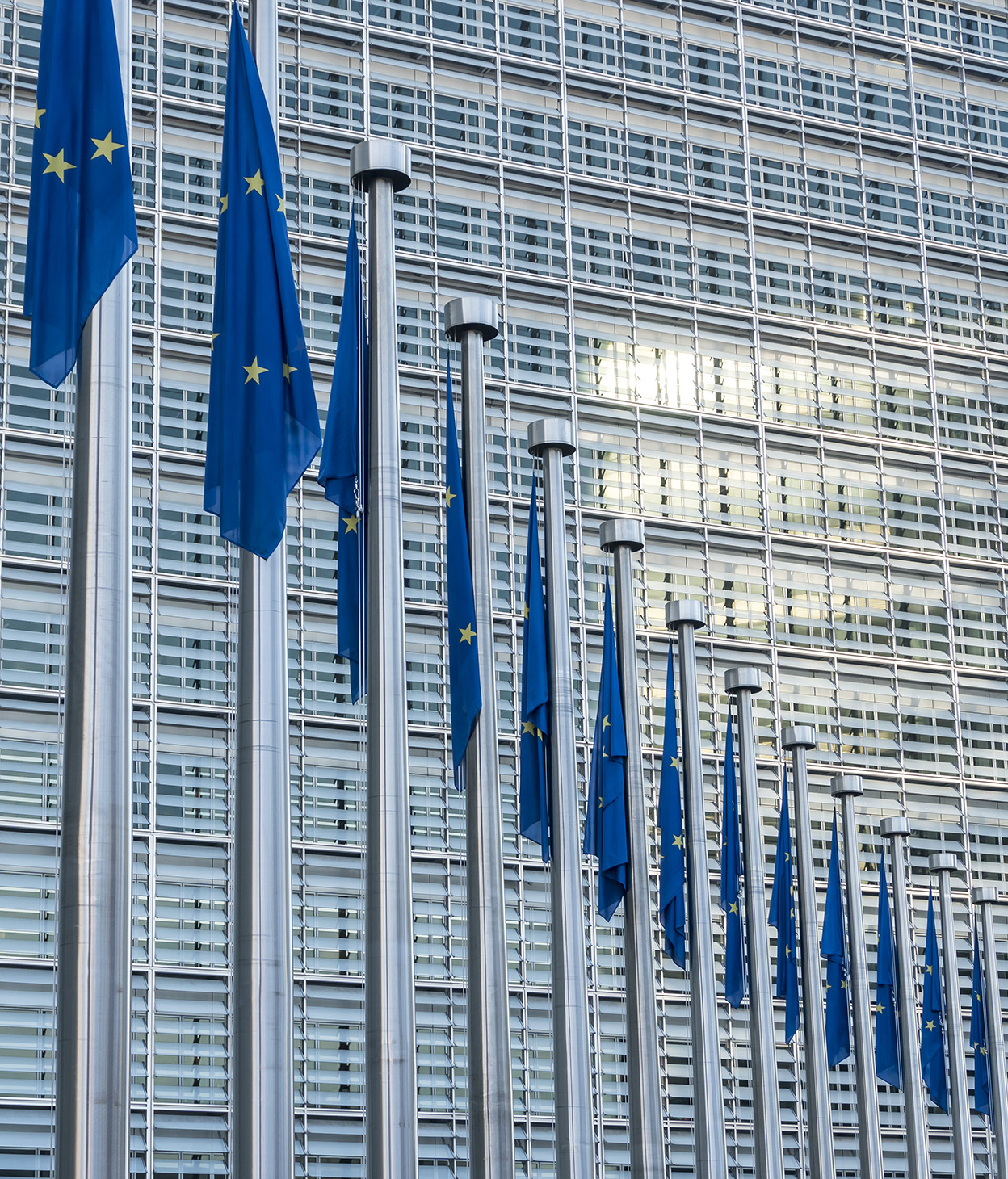

One platform for GDPR compliance and governance
Automate privacy impact assessments (PIAs) and data protection impact assessments (DPIAs) where the processing of personal data is likely to result in high risk. Get the content, templates, and integrations you need to consistently safeguard personal data.

Keep records of your processing activities by generating a central inventory of data flows. Do this through questionnaires, scanning, workshops, or a bulk import while maintaining an evergreen data catalog with automatic feeds from ongoing assessments.

For processing customer data based on consent, embed a centralized consent solution into your website, devices, and internal systems to capture consent across channels and enforce consent governance in downstream business and marketing systems.

Build and configure web forms to capture data subject access requests (DSARs) and automate the end-to-end request process from initial intake to fulfillment, including automated data discovery and redaction, or erasure, of sensitive information.

Reduce third-party risk by conducting due diligence upon initial onboarding and scheduling re-audits. Create a central record of vendors, contracts, data transfers, and security obligations by sending assessment questionnaires directly to your suppliers, service providers, or third parties.

Europrivacy is the first and only certification scheme whose criteria have been officially approved by the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) to serve as the European Data Protection Seal. As an official Europrivacy technology partner, we’re here to help you embrace privacy by design, demonstrate compliance with the GDPR, and streamline certification with the Europrivacy scheme.
Explore related resources

Webinar
Third-Party Risk
Beyond compliance: Scaling third-party risk management with automation
Join this live webinar to explore how automated vendor assessments, real-time monitoring, and compliance workflows can enhance risk insights and operational efficiency.
May 07, 2025

Infographic
Understand consent requirements in financial services
Learn how GDPR, CCPA, and more shape consent in financial services. Get clear, practical insights on compliance with our easy-to-understand infographic.
April 25, 2025
Checklist
Consent & Preferences
GDPR compliance checklist: Actionable steps for marketers
Download this GDPR compliance checklist to simplify consent management, stay compliant, and build trust. Get actionable steps tailored for marketers.
February 24, 2025

Webinar
Privacy Management
Data Privacy Day 2025
Join this webinar to hear from a panel of expert privacy professionals as they dissect the key happenings in 2024 and how privacy professionals can approach what may occur in 2025.
January 21, 2025

Webinar
Privacy Management
Revisiting IAPP DPC 2024: Top trends on the latest data protection developments
Join OneTrust and PA Consulting as we dive deeper into the key takeaways from the IAPP Europe Data Protection Congress 2024. Our speakers will provide actionable insights from the event on the latest developments in data protection, privacy, and AI.
December 12, 2024

Infographic
Privacy Automation
GDPR: Dos and don'ts
Navigating GDPR compliance can feel daunting, especially for businesses with limited resources. This quick infographic guide of actionable “dos” and “don’ts” will help you develop the foundation of a broader privacy-first approach that keeps you aligned with your GDPR compliance goals.
December 10, 2024
eBook
Consent & Preferences
Mastering GDPR consent: A marketer's guide to simplifying compliance
Learn how to simplify GDPR consent management, stay compliant, and build trust with your audience. Download this practical guide for marketers.
October 17, 2024
eBook
Privacy Management
Maturing your GDPR compliance program
This comprehensive eBook explores the key elements of a GDPR compliance program.
September 11, 2024

eBook
Privacy Management
Understanding data transfers under the GDPR ebook
In the ebook, we delve into the fallout from Schrems II and explore how organizations based in Europe can best navigate international data transfers under the GDPR.
June 05, 2024

Webinar
Privacy Management
Preparing for a new regulation: Lesson learned from the GDPR businesses can apply to the EU AI act?
Join our panel of experts as we celebrate GDPR Anniversary and take a closer look at the relationship between the GDPR and AI Act.
May 23, 2024

Webinar
Privacy Management
Navigating data privacy in 2024: Global regulatory updates & compliance strategies
Join our webinar for a comprehensive overview of the latest global data privacy regulations and updates impacting businesses in 2024 and how to prepare.
March 20, 2024

Infographic
Privacy Management
OneTrust announces partnership with Europrivacy
Learn how OneTrust and Europrivacy's partnership can help your organization achieve GDPR compliance and build trust with your customers.
December 06, 2023

Webinar
Technology Risk & Compliance
Demonstrating GDPR compliance with Europrivacy criteria: The European Data Protection Seal
Join our webinar to learn more about the European Data Protection Seal and to find out what the key advantages of getting certified.
November 30, 2023

Webinar
Privacy Management
Revisiting the ICO Data Protection Practitioner's Conference: Addressing your top challenges
Join OneTrust and KPMG UK to discuss the challenges of employee SARs, managing your breach response with third parties, and incident management.
October 25, 2023

Infographic
Privacy & Data Governance
Understanding the EU Data Boundary
Download our free infographic and get the information you need to understand the EU Data Boundary and how to properly handle data in the European Union.
September 22, 2023

Webinar
Privacy Management
Privacy in practice: PIA & DPIA with PA Consulting
Join OneTrust and PA Consulting as we discuss what makes an effective PIA, best practices, and the benefits of automation.
September 21, 2023

Webinar
Privacy & Data Governance
Privacy in practice for data mapping: With PA Consulting and Syngenta
Join OneTrust and panelists from PA Consulting and Syngenta as we explore practical ways to build an effective data mapping program, best practices, and the need for automation.
September 14, 2023

Webinar
Governance & Policy Management
EU-US DPF: What next for UK businesses?
Join our expert webinar as we discuss the upcoming UK-US DPF Extension and what UK businesses need to prepare to become DPF-certified.
September 06, 2023

Webinar
Privacy Management
Unpacking the EU-US DPF
In this webinar, we cover the new EU-US Data Privacy Framework (EU-US DPF) and what privacy program managers need to know for post-Schrems II data transfers.
June 28, 2023

Infographic
Privacy & Data Governance
The 3 priorities of the French DPO: Gain visibility, take action, automate
Download our infographic and learn about the 3 priorities of the French DPO.
May 30, 2023

Webinar
Privacy Management
GDPR turns 5: Celebrating data protection
Northern Europe panel - Join our panel of experts as they recap the GDPR, its key concepts, and what it means for organizations and compliance.
May 25, 2023

Webinar
Privacy Management
Global Panel — GDPR & Tech: Key considerations of Privacy by Design and AI in tech
Join our panel of experts as we discuss the impact GDPR had on the tech industry during the past five years, the importance of privacy by design, and what to expect with AI and regulation.
May 25, 2023

Webinar
Privacy & Data Governance
Global Panel — GDPR & Healthcare: current regulatory guidance and enforcement
In this live webinar, our expert panel examines the first five years of the GDPR, how it changed the healthcare industry, and the changing global regulatory landscape.
May 24, 2023

Webinar
Privacy Management
5 years of GDPR: Milestones, challenges, and opportunities
Eastern European panel - Watch our webinar as we look back on 5 years of the GDPR, AI, and their impact on Europe, the world, and your organization.
May 24, 2023

Infographic
Privacy Management
Comparing the FADP, Revised FADP, and the GDPR
Download our infographic to see how the Revised FADP compares with its original version and the GDPR.
May 23, 2023

Webinar
Privacy Management
Global Panel — GDPR & Retail: building customer loyalty and trust with consent and privacy
Join us for a live panel as we discuss GDPR's impact on the retail and eCommerce industry and how companies evolved to meet the global regulatory landscape.
May 23, 2023

eBook
Privacy Management
Getting started with GDPR compliance
This eBook covers the fundamental information you need to know in order to get your GDPR compliance program started and how OneTrust helps.
May 23, 2023

Webinar
Privacy Management
Global Panel — GDPR & Finance: Staying ahead of the regulatory and cyber landscape
How has the GDPR affected the financial industry? Join our live panel as we examine how it companies evolved to meet the regulatory challenges and what can be done to stay ahead of the curve.
May 22, 2023

Webinar
Privacy Automation
OneTrust and Deloitte UK - Data transfers: Assessments & safeguards
OneTrust's Center of Excellence and Deloitte UK will discuss data transfers and GDPR compliance, covering the UK stance, ICO/EDBP guidance, and more.
April 04, 2023 1 min read

eBook
Privacy Management
The 3 Priorities for DPOs in France: Gain Visibility, Take Action, Automate eBook | Resources | OneTrust
French DPOs should take three priorities into account when building their data protection and compliance programs and processes in 2023.
February 21, 2023

Webinar
Privacy & Data Governance
Data Protection in Financial Services Week: Government keynote and international transfers
This session will examine some key issues and recent developments on international data transfers with contributions from key EU, UK, and US regulators.
February 07, 2023

Webinar
Consent & Preferences
Belgian DPA approves TCF action plan: Where we go from here
Belgian DPA approves IAB Europe’s action plan to correct its Transparency & Consent Framework (TCF) violations of the GDPR.
January 12, 2023

Webinar
Privacy & Data Governance
Keeping pace with the changing regulatory landscape: UK And EU updates webinar
Learn more about the privacy updates for the UK and the EU, what to expect in the coming year, and how to manage regulatory change.
August 15, 2022

Webinar
Ethics & Compliance
GDPR and the EU Whistleblower Protection Directive webinar
Join this webinar to learn how to review your whistleblowing processes to comply with the EU Whistleblower Protection Directive, the GDPR and others.
July 06, 2022

Webinar
Privacy & Data Governance
4 years of GDPR
Watch our webinar on the last 4 years of GDPR compliance and trends for the future.
May 05, 2022

Webinar
Privacy Management
Privacy rights poland: Enhance Your DSAR process with automation, discovery & redaction
As part of our Privacy Automation webinar series, we discuss why it's important to automate DSAR fulfillment and the latest regulatory trends.
April 03, 2022

Webinar
Privacy & Data Governance
Know your laws: Comparing CCPA & CPRA vs. GDPR
Watch this free webinar and see how the CCPA and CPRA compare with the GDPR.
January 04, 2022

Checklist
Privacy & Data Governance
Transfer Impact Assessment (TIA) checklist
This Transfer Impact Assessment checklist provides an overview of the key steps you can take as you perform a TIA.
December 01, 2021

Infographic
GDPR's 8 fundamental data subject rights
Download our GDPR's 8 Fundamental Data Subject Rights infographic and learn more about the individual rights guaranteed under the EU's major privacy law.
August 27, 2021

eBook
Privacy & Data Governance
The ultimate guide to GDPR compliance
Download this eBook to get an ultimate guide to understanding the GDPR and implementing steps towards compliance.
August 26, 2021

eBook
Privacy & Data Governance
10 steps to meeting the GDPR Article 30 requirement
Download this eBook and learn how to leverage data mapping for your GDPR Article 30 compliance program.
July 22, 2021

White Paper
Privacy Automation
Mastering PIAs & DPIAs: A complete handbook for privacy experts
Unlock the full potential of your privacy program with our complete handbook designed to equip privacy professionals with the essential tools and knowledge for establishing robust PIA and DPIA processes.
July 22, 2021

Checklist
Privacy & Data Governance
GDPR compliance checklist
Download our GDPR compliance checklist for recommendations on improving your organization's privacy program.
June 11, 2021

Webinar
Privacy Automation
PIA and DPIA demo webinar with Data Privacy Group
Join our webinar to learn the benefits of automating your PIAs and DPIAs using the OneTrust platform
FAQs
We’re here to help demystify the world’s most comprehensive data protection directive. Explore answers to frequently asked questions below.
Our global contributor network of lawyers, researchers, and translators provide contextually relevant updates from the desk of the supervisory authority to your data protection officer (DPO) via the OneTrust platform, so your privacy program management activities consistently map to the latest GDPR requirements.
Leverage our built-in business intelligence engine to automate compliance reporting as well as KPIs and Board reporting to demonstrate the value your program provides in the protection of personal data.
Additionally, as an official Europrivacy technology partner, we can help you build external trust in your data processing activities by certifying compliance with the GDPR and other applicable European data protection regulations.

