The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) was published in January 2020 by the US Department of Defense. The model established a new method to evaluate vendor cybersecurity programs by measuring both technical controls in place and ongoing processes to review. The initial CMMC 1.0 reflects a collaborative approach by sampling practices across leading IT risk management frameworks, cloud security and others to deliver a comprehensive model based on the latest local cyber-community insights with a global perspective. Recently, the US Department of Defense released a new CMMC proposal based on findings from an internal program assessment. The proposal deemed CMMC 2.0, announces a new strategic direction for the CMMC which aligns the CMMC to more closely reflect NIST SP 800-171 and NISP SP 800-172. Let’s take a look at what’s new:
What’s new in CMMC 2.0?
According to the US Department of Defense’s announcement, the updates to the CMMC strive to simultaneously simplify and strengthen the security of the defense industrial base. The announcement sites new goals as:
- Empowering a more collaborative nature between industries.
- Integration with acquisition programs to ensure that contractors meet requirements.
- Threat-informed defense industrial base (DIB) enhancements.
- Simplifying and clarifying suggestions around regulation, policies, and contracts.
- Additional advanced focus on third-party and cybersecurity requirements.
- Pivoting to a standard that threads trust as a unique fabric of the CMMC.
Overall, the new approach maintains the goals of the original model, while providing further clarity and emphasis on the criticality of implementing strong cybersecurity practices as the threat landscape continues to evolve.
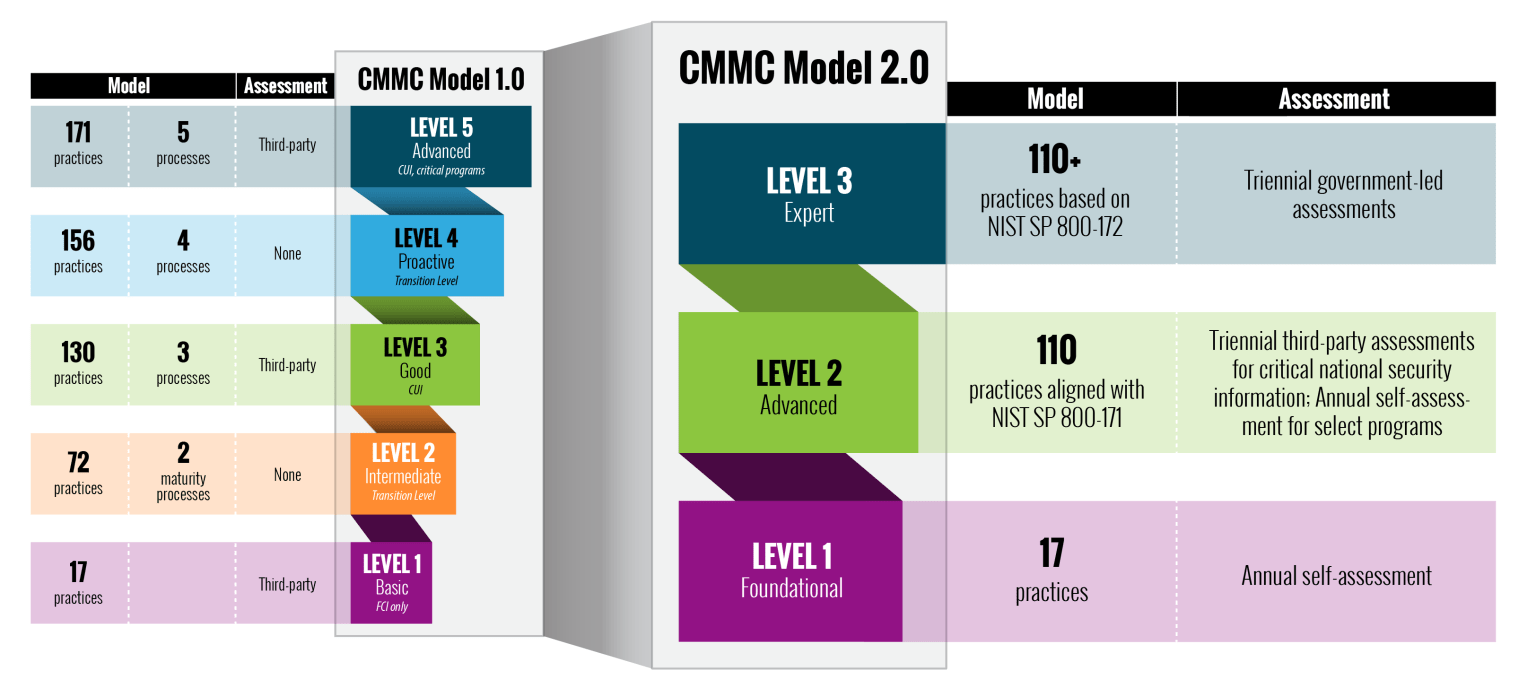
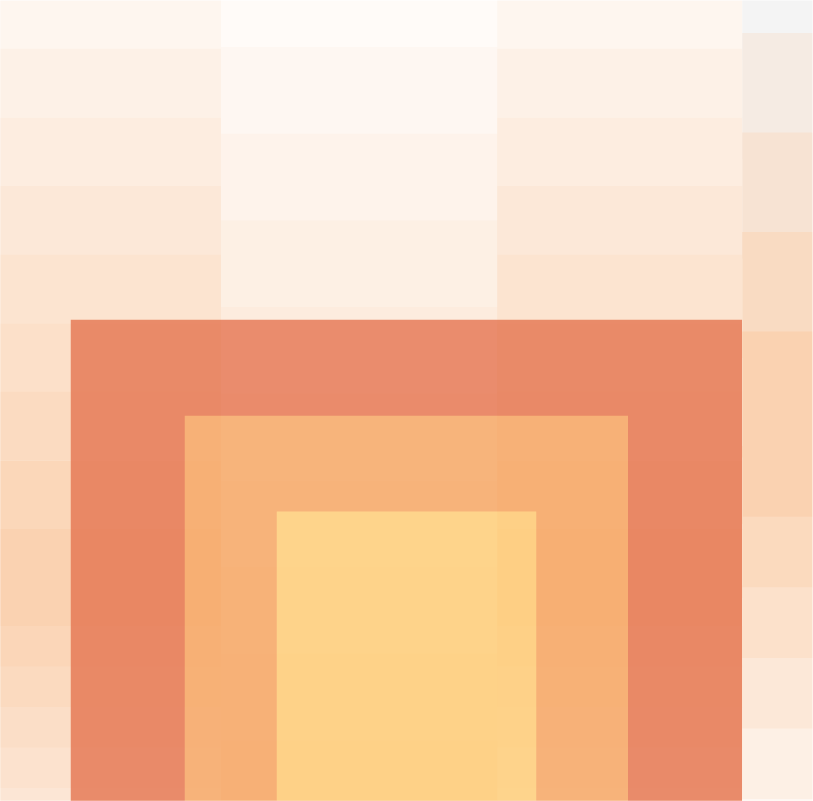
A model of simplification
Specifically, CMMC 2.0 scales the model down from a 5-tiered model to a 3-tiered model. See the image below for more detail.